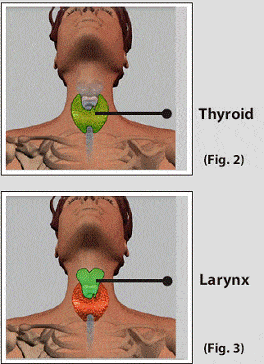
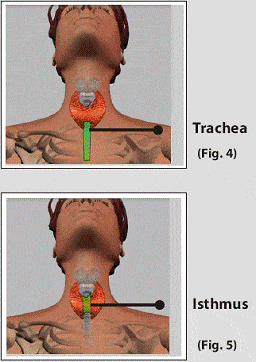
Thyroid gland is a butterfly shaped gland located in the front of the neck below the voice box. It is composed of two lobes, one on each side of the windpipe. The lobes are joined together by a narrow band of thyroid tissue called the isthmus.
Thyroid gland secretes hormone called thyroxin that help regulate the body’s metabolism and levels of calcium. Thyroid hormones affect development during growing period, breathing, heart and nervous system functions, body temperature regulation, muscle strength, skin dryness, menstrual cycles, weight, and cholesterol levels. There are number of conditions that need removal of thyroid gland as part of the treatment.
When do you need to see thyroid surgeon?
- Overactive thyroid gland that does not respond to other form of treatment
- Nodule in the gland suspicious of thyroid cancer
- Enlarge thyroid gland pressing on the windpipe or oesophagus
- Thyroid gland swelling descending to the chest cavity
- Thyroid swelling which is not cancer but noticeable to naked eye
Thyroid lobectomy
Multinodular goitre
When the thyroid gland is enlarged and visible to naked eye it is described as goitre. Thyroid hormone contain large amount of iodine. When there is less iodine available thyroid gland get bigger to compensate for lack of iodine. Lack of iodine is mostly due to diet poor in iodine or specific enzyme deficiency in synthesis of thyroid hormone or occasionally due to genetic defects. Thyroid gland gets intermittently and progressively become larger with formation of multiple nodules in the gland. Enlarged thyroid can put pressure on wind pipe, oesophagus and nerve to voice box. If not treated early, gland can descend to chest cavity. Your surgeon will be able to evaluate the size and complications caused by multinodular goitre and advise on surgical treatment.
Thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is an abnormal growth of the cells of the thyroid gland. Thyroid cancer is more common in women than men. People who are exposed to high levels of radiation to the neck and have a family history of thyroid cancer and goitre (enlargement of thyroid gland) are at a higher risk of developing thyroid cancer.
There are different varieties of cancers developed in thyroid gland. However more than 90% of cancers belong to category called differentiated thyroid cancer (papillary cancer, follicular cancer) and have very higher rate of cure by surgery.
Generally, surgery involving thyroid gland removal is the most common treatment of thyroid cancer. Total thyroidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove all of the thyroid gland. Subtotal thyroidectomy is a surgery to remove part of the thyroid gland. Your doctor may also remove the lymph nodes if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. The surgery is performed under general anaesthesia. The surgeon removes the thyroid gland by making a 2- 5 cm incision in the middle of your neck, on top of the thyroid gland. A small tube (catheter) will be placed into the area to drain the accumulated blood and fluids. After thyroidectomy supplementary thyroid hormone is given as a tablet that need to be taken once daily in the morning.
Nerves to the voice box travel close to the thyroid glands and during thyroid surgery these nerves are identified and preserved. Also there are four tiny glands called parathyroid glands placed behind the thyroid gland need identification and preservation. These glands control calcium level in the blood and damage to them can cause drop in calcium levels after the thyroid surgery.
It is important to select a surgeon who has long experience of thyroid surgery and discuss all options prior to undergoing thyroid surgery.