Salivary Gland Surgery
Salivary glands secrete saliva to mouth which facilitate mixing of food and swallowing. There are three pairs of major salivary glands. Surgical removal of salivary gland may be required when there is abnormal growth, block of salivary ducts opening due to salivary calculus or gland is affected by frequent attacks of infection.
Parotid glands
There is a pair of parotid salivary glands in the cheek in front of the ear. Gland has two components, deep and superficial lobes. Facial nerve which is responsible for movement of facial muscles runs between these two lobes. Salivary gland excision is required when there is abnormal growth in the gland. Most of the swellings are in the superficial lobe and careful preservation of facial nerve is required as part of the surgical excision of parotid gland.
Sub mandibular gland
As in parotid gland, Sub mandibular gland also has superficial and deep parts. Deep part is in the floor of the mouth under the tongue and superficial part is hidden under the cheek bone. It is common for the gland to get blocked by salivary calculus. Abnormal growth is less common than parotid glands. Gland is excised by incision placed in the upper neck.
Lingual Glands
Lingual salivary glands are in the floor of the mouth under the tongue in front of submandibular gland. Rupture of duct can release saliva to the floor of the mouth causing condition called ranula. This condition can be corrected by removing lingual gland on the floor of the mouth without having skin incision.
Lymph node biopsy
Lymphatic system is part of immune system composed of tiny network of tubes called lymphatic ducts and small nodules called lymphnodes. Tissue fluids generated by various organs are collected by lymphatic tubes and they get filtered at lymph nodes. Lymph node has large number of cells called lymphocytes and which has an ability fight against infection and recognizing foreign materials.
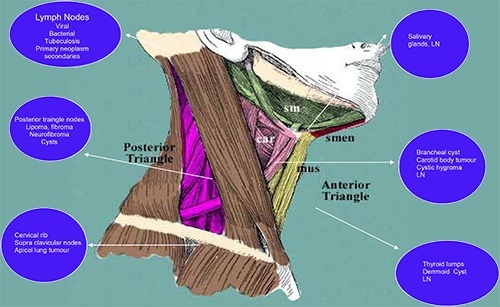
There are large numbers of lymph nodes in the neck. They can get enlarged due to infection, cancer and some degenerative disease. One of the enlarged nodes can be removed for examination by simple procedure call lymph node biopsy. However, as there are large number of important nerves, blood vessels and other organs travelling in the neck biopsy should be done without damaging to those important structures.
Lymph node dissection
Block dissection of neck node
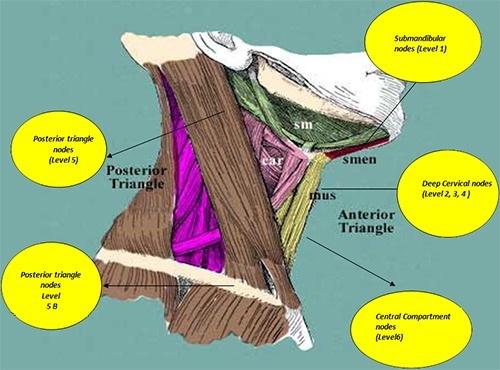
Most of abnormal growths in the head and neck area first spread to the lymph nodes, from their primary site of origin. Depending on the primary site of the tumour the area of lymph nodes involved can be predicted. Lymph nodes in the neck are classified into various groups. For example oral cancers tend to spread to lymph nodes under the jaw bone and thyroid cancers spread to the nodes in the central part of the lower neck. In cancer operations in the neck primary growth and group of lymph nodes involved are removed as one mass. Removals of one or few groups of nodes are called block dissection. Your surgeon will be able to describe the area of lymph node dissection depending on the primary site and stage of the lesion.
Excision of other neck lumps
Relative to other parts of the body neck is narrow and contain less space. However there are important structures in the neck which connect head and face to rest of the body through the neck. There are important blood vessels, nerves, breathing organs, swallowing tubes, muscles and lymph nodes connecting head to the rest of the body across the neck. Neck lumps can arise from any of these organs and because of that neck is common place to find abnormal lumps and bumps.
In children neck lumps are commonly due to developmental defects. Branchial cyst, Dermoid cyst and cystic hygroma are fluid filled cysts. Sternomastoid tumour is due to thickening in the muscle. Thyroglossal cyst develops from developmental defect of thyroid gland.
There are large numbers of lymph nodes in the neck. A swelling of a lymph node is commonest lump found in the neck. Swelling could be due to infection, spread of cancer to a lymph nodes or disease of lymph nodes itself. Surgical excision of node is required to confirm diagnosis.
Your doctor will diagnose the neck swelling by physical examination. If your doctor suspects a nodule or a cyst, then ultrasound, CT scan of the head and neck or biopsy will be required to confirm the presence and define the type of tumour to provide the necessary treatment. Depending on the diagnosis some lumps need to be treated by surgical excision.